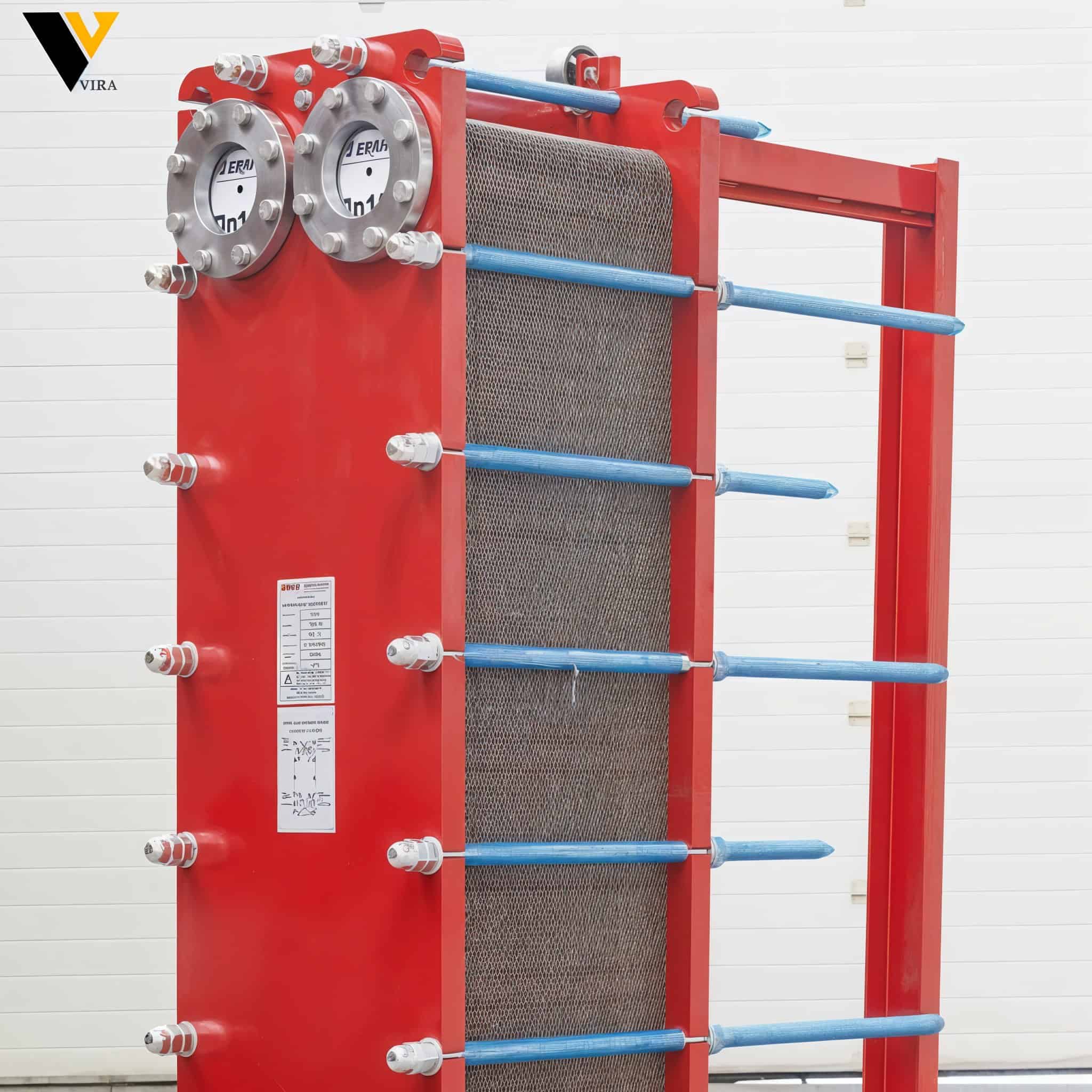
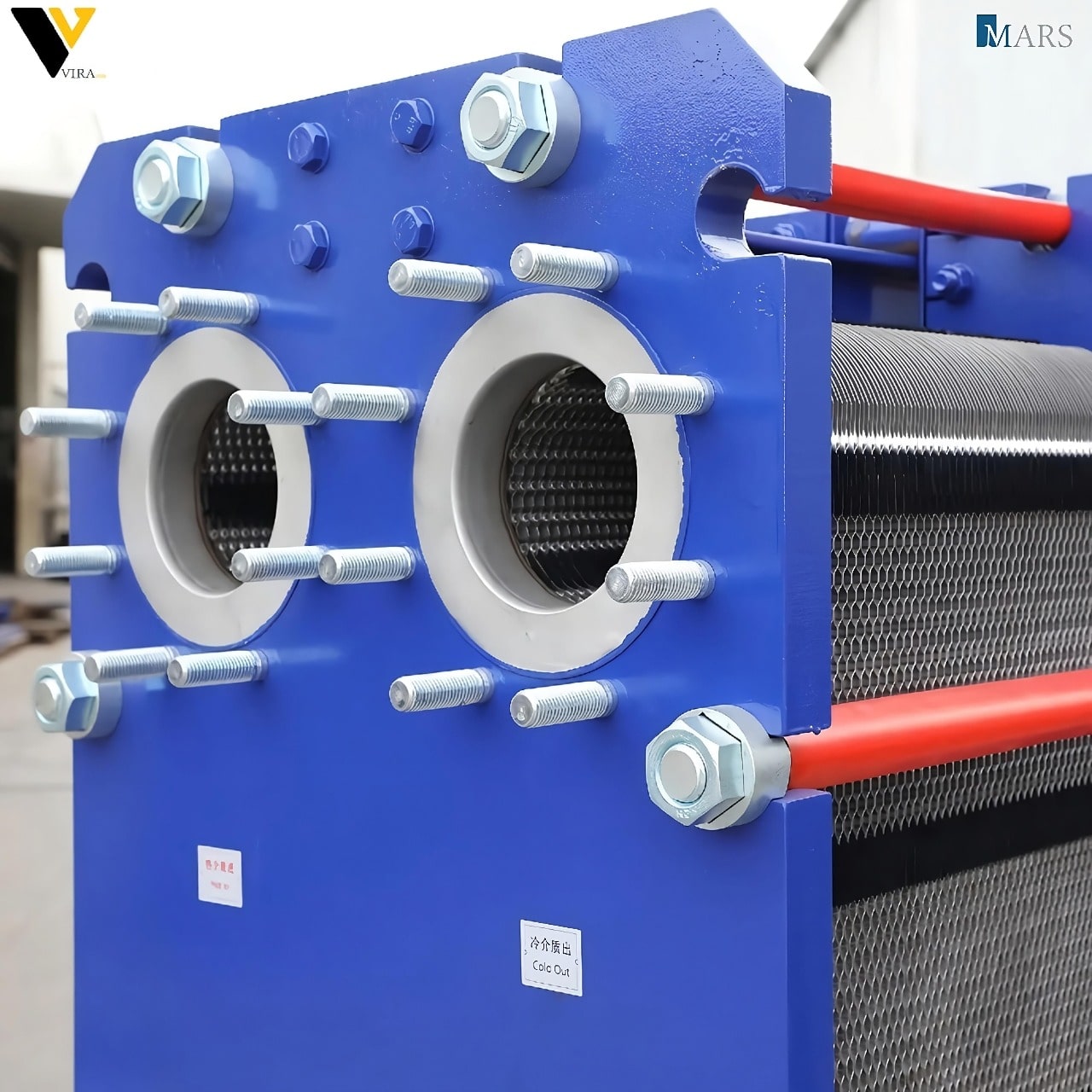
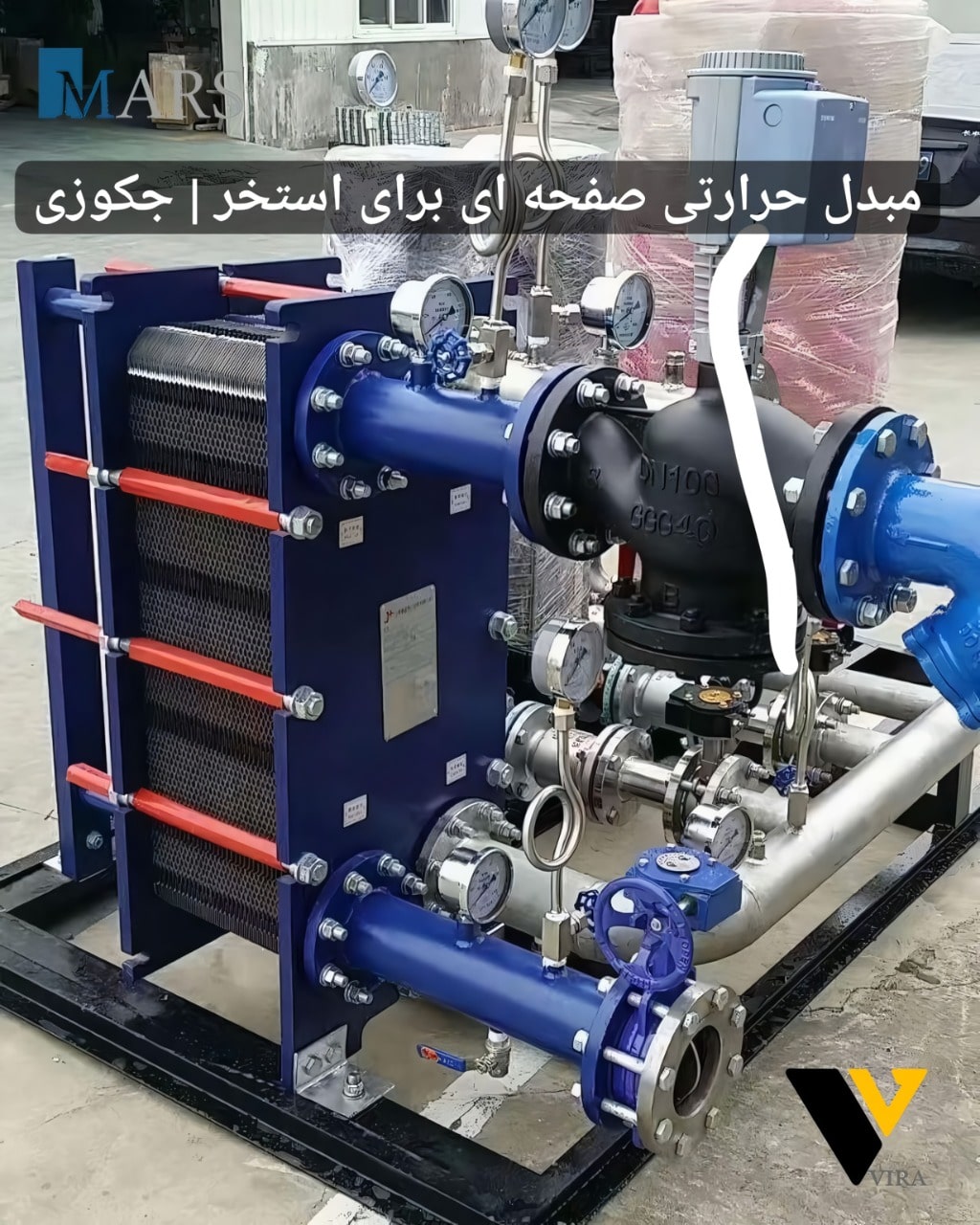
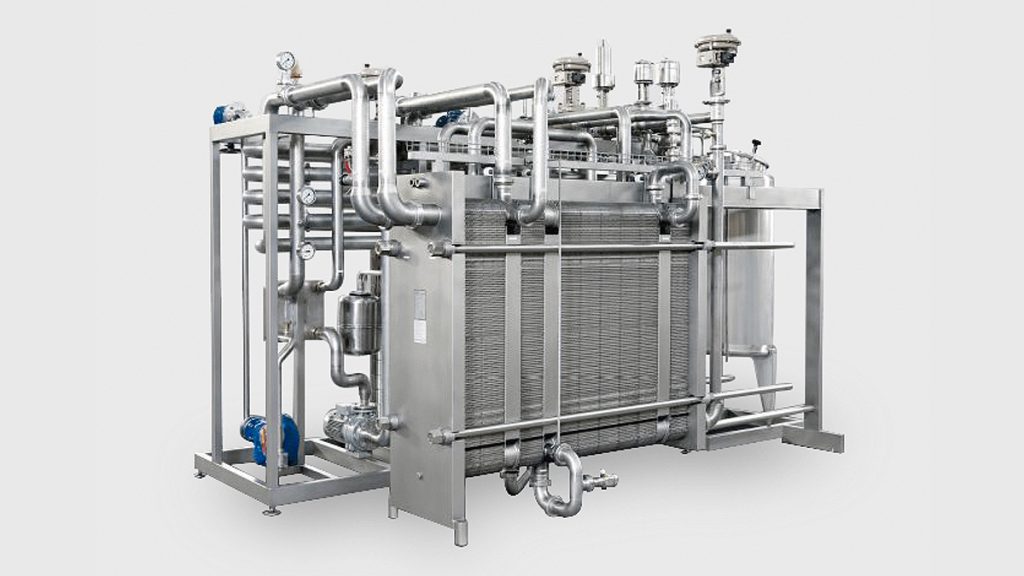
:Introduction
In industries and commercial facilities where cooling is essential, ice banks play a vital role in energy management and process efficiency
These systems store cooling energy in the form of ice, which can be used later during peak demand
But what exactly is an ice bank, and how does it function? This article will explore the mechanism, applications, advantages, and technical aspects of ice banks — ideal for engineers, facility managers, and energy consultants.
ICE BANK
Premium Ice Bank Manufacturer
Looking for a reliable Ice Bank manufacturer? We specialize in designing and producing high-efficiency ice bank systems tailored to your specific cooling needs. Whether for dairy, HVAC, or industrial use, our tanks are built to deliver consistent performance and long-term savings.
✔ Custom sizes available | ✔ Energy-efficient design | ✔ Direct factory pricing

?What Is an Ice Bank
An ice bank is a thermal energy storage system designed to accumulate cooling energy by freezing water into ice during off-peak hours (usually at night), and then use that stored energy during peak hours (usually during the day) to cool air or fluids
?How Does an Ice Bank Work
:Here’s a step-by-step overview of the ice bank’s working cycle
:Charging Phase (Night)✅
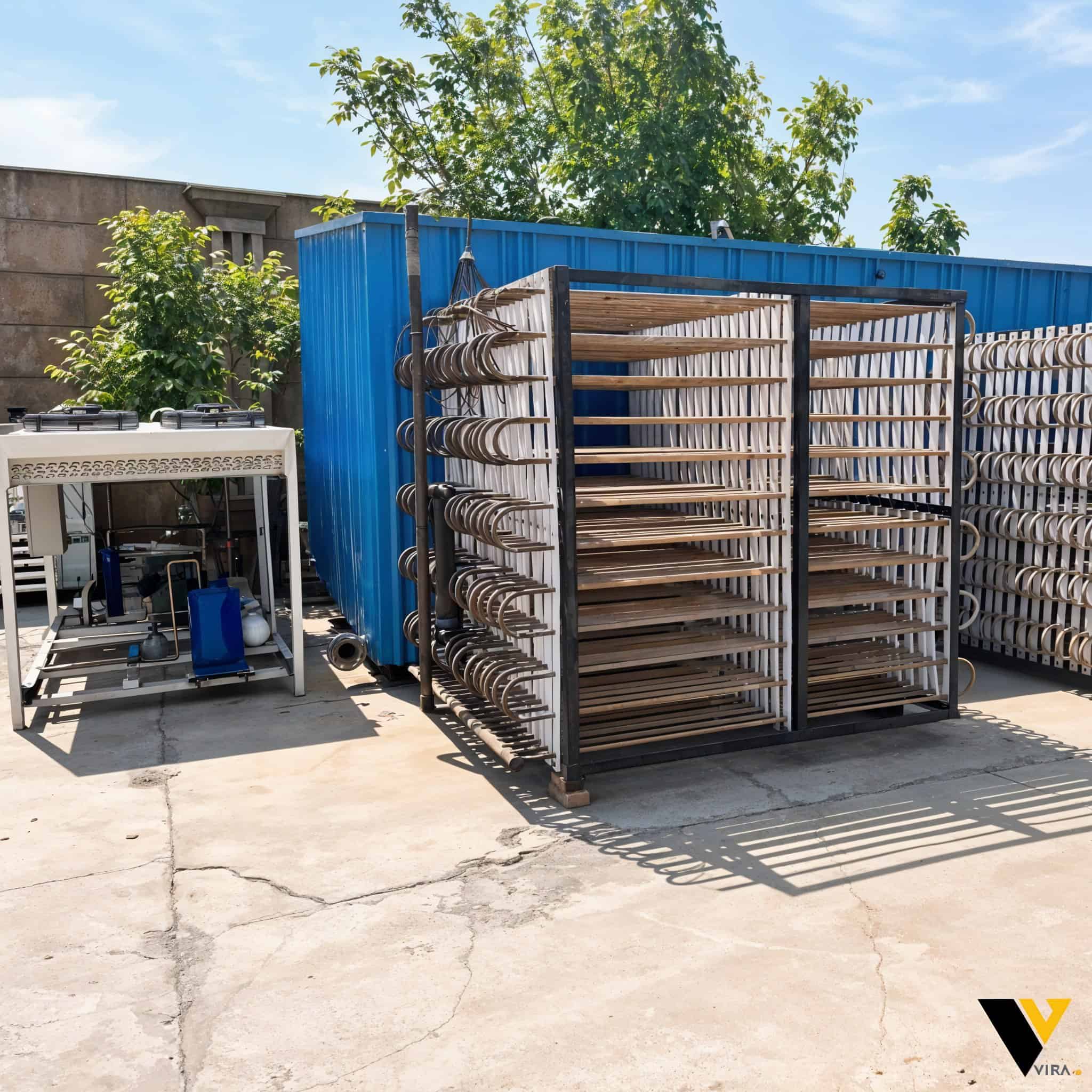
A chiller or refrigeration unit cools a stainless steel coil submerged in water
Water around the coil begins to freeze, forming ice on the surface of the coil
This process continues until a thick layer of ice builds up
:Discharging Phase (Day)✅
Warm fluid (typically glycol or water) flows through the ice-covered coils
The ice melts, cooling the fluid without engaging the chiller
The cooled fluid is used for HVAC, process cooling, or dairy tank chilling

Table: Ice Bank System Overview
| - | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Store and deliver cooling energy | |
| Storage Medium | Ice (frozen water) | |
| Energy Source | Electric chillers (off-peak electricity) | |
| Cooling Delivery | Indirect through melted ice-cooled fluid | |
| Common Uses | Dairy cooling, HVAC systems, beverage & food plants | |
| Energy Saving | Up to 40% reduction in peak energy usage | |
| Tank Material | Stainless steel, polyethylene, insulated for storage |
:Benefits of Ice Banks
.Peak Load Shifting: Use electricity at night when rates are lower✅
.Energy Savings: Reduce demand charges and operational costs✅
.Environmental Impact: Supports grid stability and lower carbon output✅
.Reliable Cooling: Even during chiller maintenance or failure✅
.Flexible Applications: From dairies to district cooling networks✅

:Common Applications
.Dairy Farms – Milk chilling to 4°C before transfer🥛
.Commercial HVAC – Air conditioning large buildings🏢
.Industrial Processes – Brewery fermentation, meat processing🏭
.Beverage Plants – Carbonated drink cooling🍺
.District Cooling – City-wide energy management systems🌆
:FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
❓ What is the typical capacity of an ice bank
Capacities vary widely — from 1,000 to 50,000 liters, depending on the application
❓ How long does the ice last
Most ice banks are designed to deliver 8–12 hours of cooling depending on load and size.
❓ Is it cheaper than a traditional chiller
Yes, especially when considering energy savings and off-peak electricity rates
❓ Can I retrofit an ice bank into my existing system
Yes. Many manufacturers offer custom retrofitting solutions
❓ Who manufactures ice banks
Top manufacturers include Alfa Laval, GEA, Danfoss, and regional suppliers in Iran, China, and Europe

:Conclusion
An ice bank is not just a tank full of ice—it’s a smart, strategic component of modern energy systems
It offers significant benefits in energy savings, sustainability, and cooling reliability. As energy costs rise and sustainability becomes a priority, more industries are turning to ice banks as a cost-effective thermal energy storage solution
Whether you’re managing a dairy farm, running a factory, or looking for HVAC energy efficiency, investing in an ice bank system can deliver measurable returns